We use affiliate links to run our site. When you buy through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission, without any added cost to you. Learn more
In some of my earlier articles, I have mentioned pH and the ideal pH for a particular plant. But many starters are not aware of this technicality. So I decided to demystify the jargon in this article and explain what different pH levels in the soil mean.
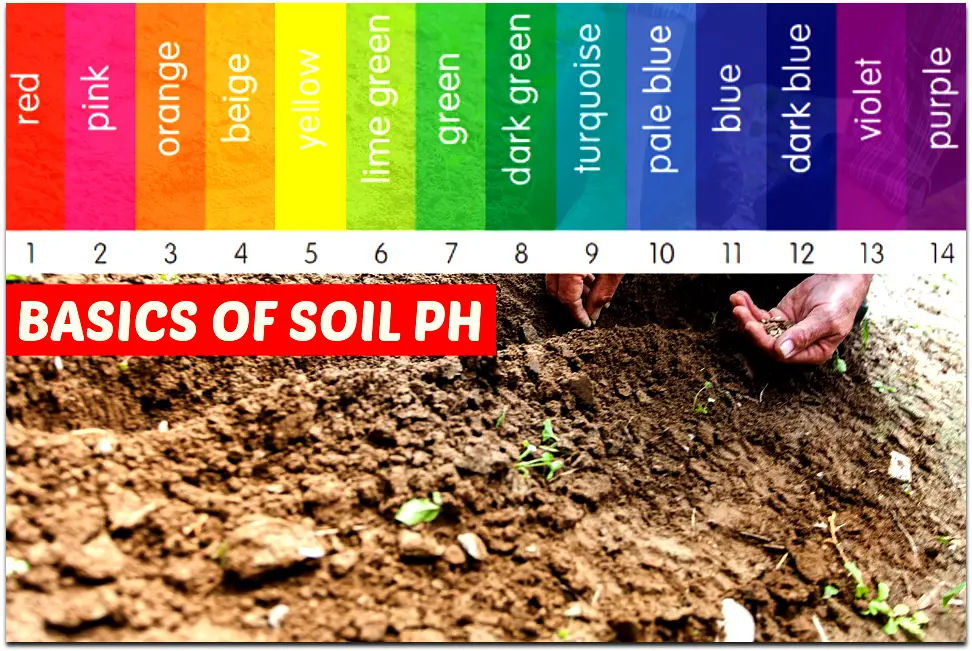
What is Soil pH?
Soil pH is the measure of how acidic or how alkaline your soil is. It is actually to measure the concentration of Hydrogen ions in the solution.
The ph levels are measured on a scale of 0 to 14. Where 0 being the most acidic and 14 is the most alkaline and 7 stands for neutral.
To give you an example lemon juice can be in the range of 2 to 3 signifies very acidic whereas baking soda can be of a pH of 8 to 9 which means it is very alkaline. The fresh clean drinking water is pH 7.
This pH is calculated on the logarithm scale so a difference between one point is equal to 10 times acidity. i.e, the pH of 6 is 10 times more acidic than pH 7 and 10 times less acidic than pH 5.
Why Calculating Soil pH is Very Important?
Now you must be wondering why pH is so important to your plant? Let’s see why.
The pH of the soil has a very big role in plant growth and its survival. Though soil pH is not a nutrient, it controls the availability of nutrients to the plant. Soil acidity has a tremendous influence on the structure, and breakdown of organic materials in the soil. It also impacts the life of soil microbes.
For example, a soil pH of 6 or more can inhibit the absorption of calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium etc. whereas a soil pH of 7.5 or more can reduce the amount of Iron, Zinc, Copper, Manganese.
A pH level of less than 4 can be full of toxic amounts of Aluminum or Manganese.
So it does not matter how much nutrient you put into the soil, if it can not get absorbed by the plant it is of no use. A pH that is too low or too high can be fatal for your plants, so it is very important that you get it right.
How To Change pH Levels of Soil:

Now the good news. The soil pH is not fixed. You can change it to your plant’s liking.
The soil pH is dependent on your local climate. You can get the idea by looking at the plants in your locality. Generally, it is found that in high rainfall areas the soil pH is acidic.
Plants like blueberries flourishes in these areas. Whereas typically low rainfall areas in the world generally contain alkaline soil. Plants like olive or pomegranate do well in those areas.
It is best to test your soil pH before you start planting. You can get the required instruments in your local garden shops or you can buy them online. You can also contact any professional to do it for you.
If your soil is too acidic and you want to reduce the acidity and increase the pH, agricultural lime or dolomite can be a good option to be added to the soil. Generally agricultural lime is cheaper than dolomite. In case your soil is deprived of magnesium then add dolomite otherwise lime would be fine.
In case your soil is far more alkaline and you want to decrease the pH, add peat moss or compost. Adding these organic materials can definitely beneficial than adding ammonium sulfate or other inorganic sulfates.
I hope this clears the doubts surrounding the pH and its effect. Do post your comments.
If you like the post don’t forget to PIN IT

Amazon and the Amazon logo are trademarks of Amazon.com, Inc, or its affiliates.

Hi there! My name is Prasenjit and I’m an avid gardener and someone who has grown a passion for growing plants. From my hands-on experience, I have learned what works and what doesn’t. Here I share everything I have learned.
1 thought on “What is Soil pH: This Is Why Soil pH is Important For Your Garden”