We use affiliate links to run our site. When you buy through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission, without any added cost to you. Learn more
The secret to a lush vegetable garden isn’t always sun-beaten soil but occasionally cleverly placed shade. We’re forever focused on getting better yields, and have forgotten the joys of using shade wisely. Have you ever watched your lettuce wilt in the summer sun, or your spinach bolt before it was even ready for harvest? Well, you’re not alone!
Shade gardening is not just about protecting plants; it’s about creating a microclimate in which everything can really thrive.
In this guide, we’ll show you ways that the addition of shade can increase productivity in the garden and share simple strategies for maximizing your space. We will guide you through the science, the strategies, and the step-by-step tips to maximize the power of shade. By the time you finish, you will learn how to grow better plants and increase your harvest!
What Are Shade Structures?
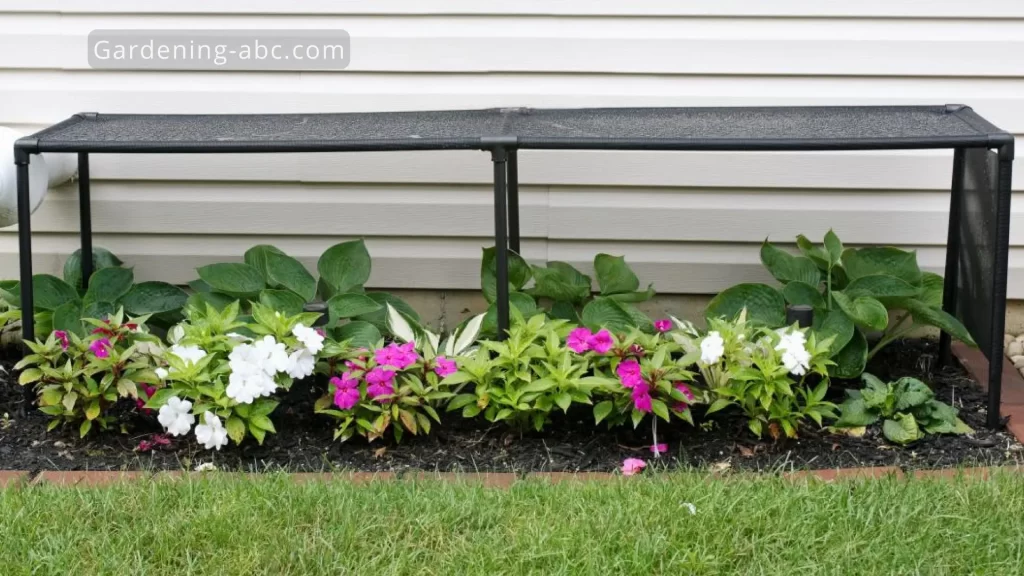

Shade structures are any barriers—think cloths, trellises, or even tall companion plants—that filter sunlight before it reaches your crops. Their main job? Shielding your veggies from excessive heat and harsh UV rays.
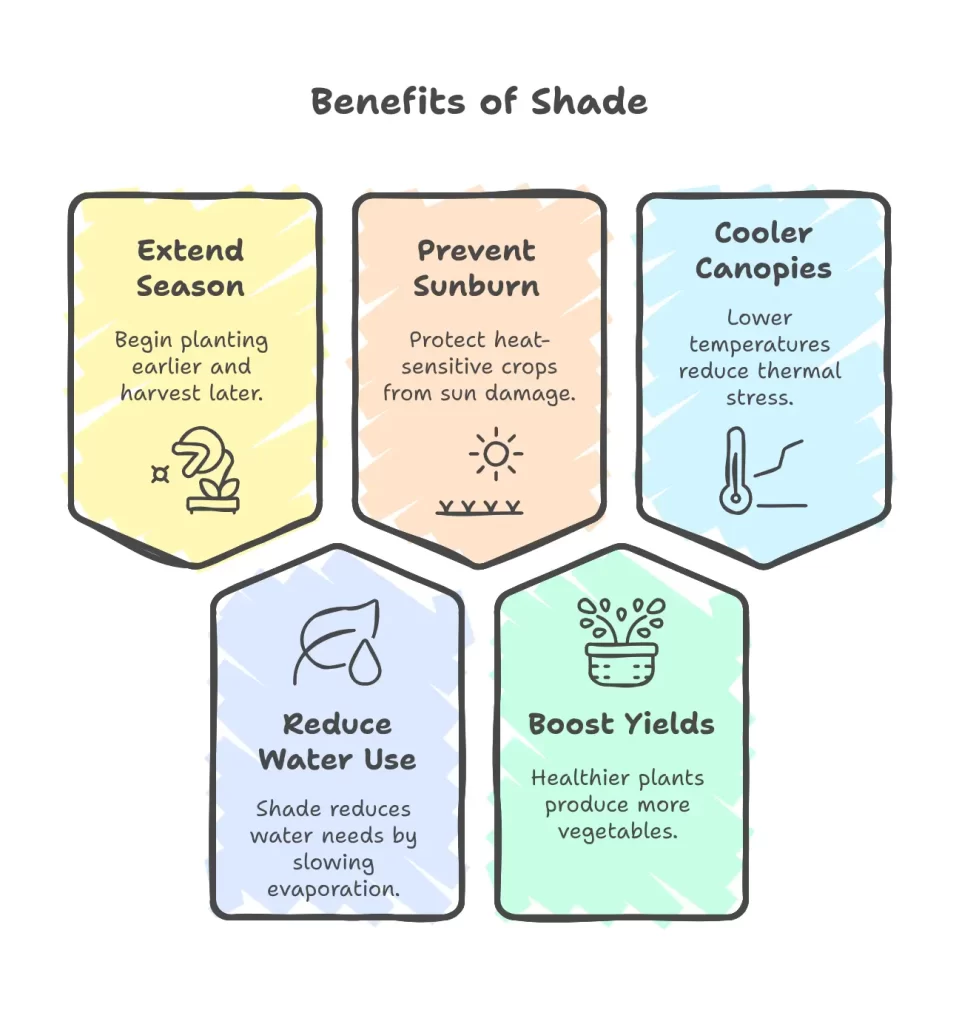
Why It Is Important:
- Extend the growing season: Start earlier in spring and harvest later into fall.
- Slash water use: Shade can reduce water needs by up to 40% by slowing evaporation.
- Prevent sunburn and wilting: Especially crucial for heat-sensitive crops.
- Boost yields: Healthier, less-stressed plants mean more veggies for your table.
- Cooler canopies: Lower temperatures under shade mean less thermal stress and happier plants.
Fun fact: According to a 2024 study by the University of Arizona, shade structures can increase lettuce yields by up to 25% in hot climates!
Which Vegetables Thrive in the Shade (and Which Don’t)?
Not all vegetables respond equally to shade, so understanding crop-specific needs is crucial for success. Shade-loving vegetables benefit from reduced light intensity, which slows bolting and promotes tender growth, while sun-dependent crops require more direct exposure to thrive.
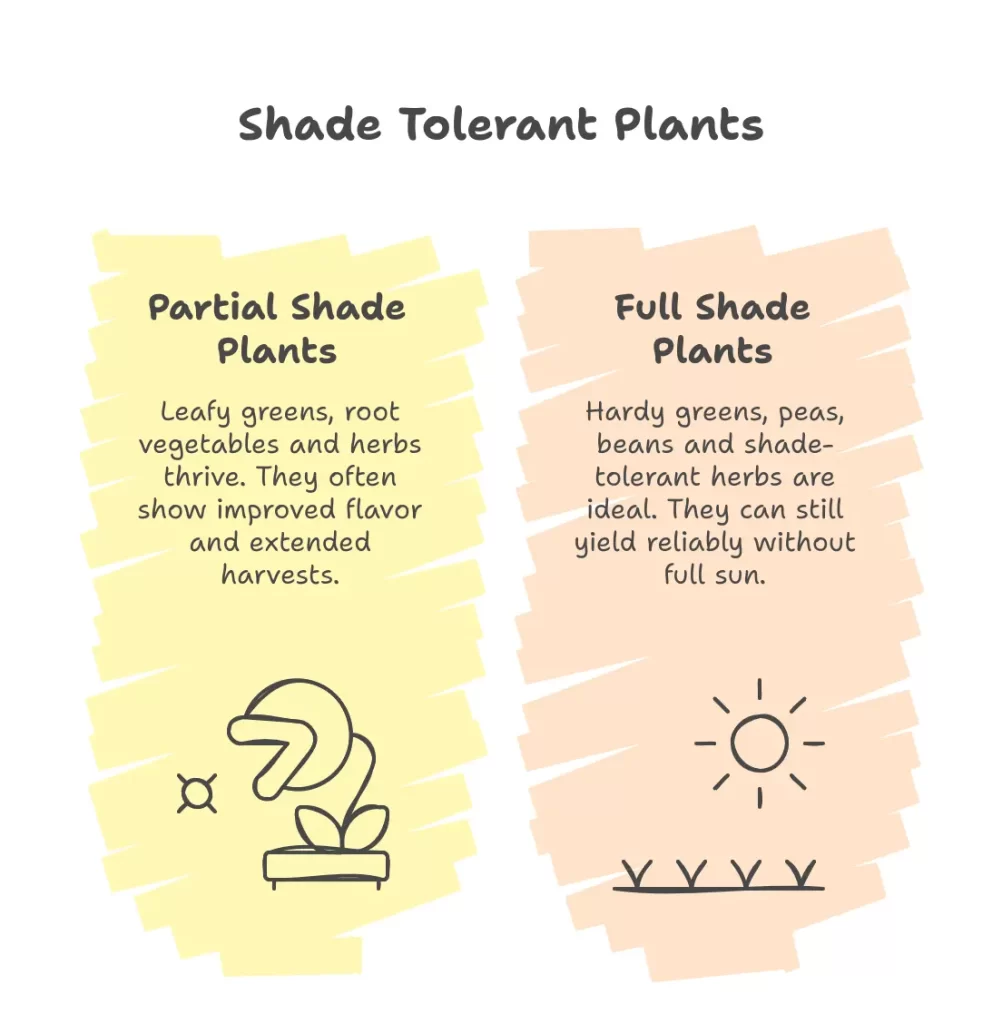
Shade-Loving Vegetables:

- Partial Shade (4-6 hours of sun): These include leafy greens like lettuce, spinach, kale, arugula, and chard, which flourish in cooler conditions and can produce flavorful, nutrient-rich leaves. Root vegetables such as radishes, carrots, and beets also perform well, though their growth may be slightly slower, resulting in smaller roots. Herbs like mint, lemon balm, oregano, and basil thrive here, often showing improved flavor and extended harvests.
- Full Shade (2-4 hours or less): Options are more limited but include hardy greens like arugula and Swiss chard, as well as certain peas, beans, and shade-tolerant herbs such as Vietnamese coriander. These crops are ideal for underutilized garden spots, where they can still yield reliably without full sun.
- Plant Umbrellas for Outdoor Plants: In the…
- Angle Adjustable & Durable: The bendable spring at…
- Larger and Higher Garden Plant Umbrella: Each…
Vegetables That Do NOT Grow Well in Heavy Shade:
Fruiting vegetables like tomatoes, peppers, and eggplants demand at least 6 hours of direct sunlight for proper fruit development, as insufficient light hinders photosynthesis and leads to poor yields. In heavy shade, these plants often become leggy and unproductive, with reduced fruit set and quality.
Why it matters: Planting the right crops for your shade level is the first step to success—and prevents disappointment at harvest time!
How Much Shade is Just Right?
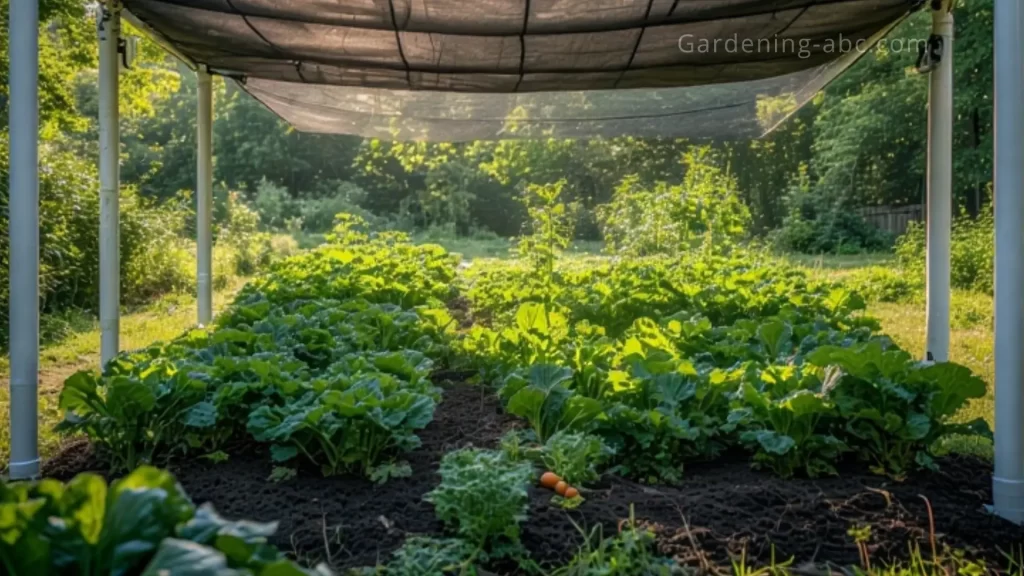


Finding the optimal shade level involves balancing light reduction with the need for photosynthesis, which directly impacts growth and yield. A general recommendation is to use shade cloths with a 30-50% shade rating, which can reduce temperatures by 10-15°F while allowing enough light for healthy development.
For heat-sensitive crops like lettuce and spinach, up to 60% shade during peak heat can prevent bolting and maintain quality, though 30-50% is often ideal. Fruiting vegetables like tomatoes may only need 20-30% shade during the hottest periods to avoid stress without compromising yields.

Morning sun with afternoon shade is typically best, as it minimizes midday heat while supporting energy production. Always observe your plants and adjust based on local conditions, as over-shading can reduce photosynthesis efficiency and lead to weaker growth.
Pro tip: Watch your plants! If leaves look pale or stretched, reduce shade. If they’re wilting or scorched, add more.
Types of Shade Structures:
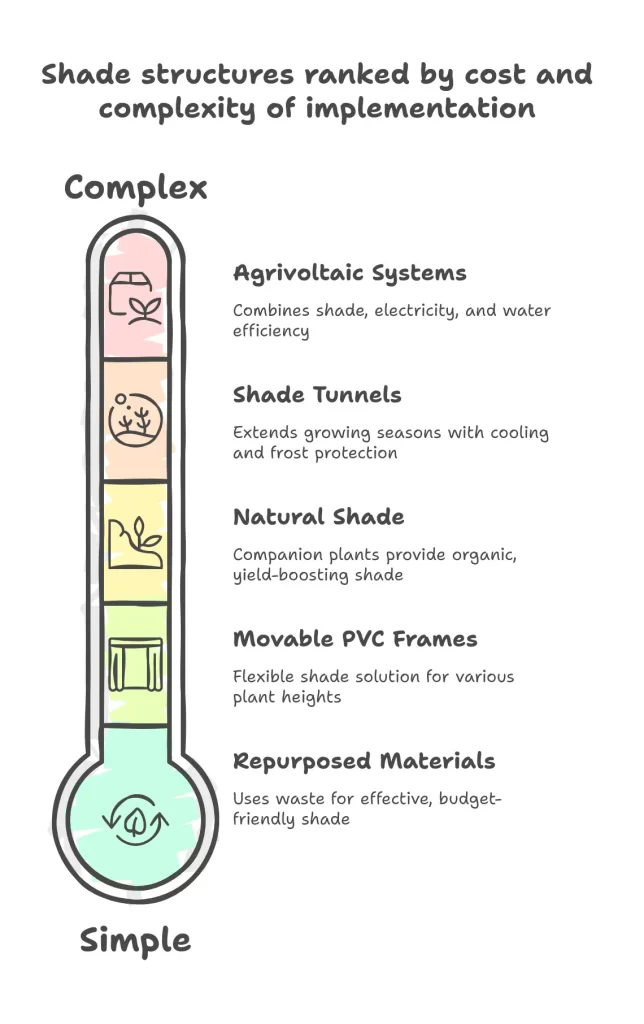
Shade strategies range from simple, budget-friendly options to advanced systems, allowing flexibility based on your resources and needs.
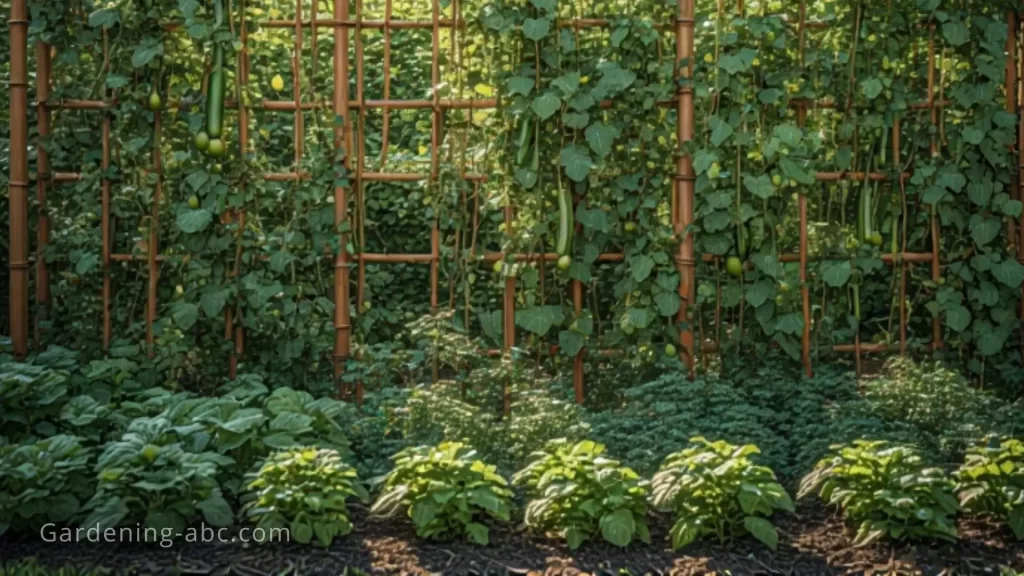


- Budget-Friendly Options: Repurposed materials like old screens or mesh fabric, PVC pipe frames (under $30 for a 4×8 ft setup), pallet wood for lath houses, or bamboo trellises provide effective shade without high costs.
- Movable Shade Structures: Lightweight PVC frames with shade cloth can be repositioned easily, making them ideal for A-frames over low crops or arched hoops for taller plants.
- Agrivoltaic Systems: These combine solar panels with vegetable beds, offering shade while generating electricity and improving water efficiency by up to 40%. Panels should be 8-10 feet above crops to allow about 70% ambient light.
- Shade Tunnels: These provide a greenhouse-like environment with added cooling, extending seasons by 2-3 weeks and protecting against frosts.
- Natural Shade (Companion Planting): Planting sunflowers or corn alongside heat-sensitive vegetables can increase overall yields by 15-20% through natural shading.
Fun fact: A 2025 study in “Horticulture Science” found that companion-planted shade increased basil yield by 18% compared to unshaded beds.
How to Apply Shade for Optimal Growth


Timing shade application is critical to maximize benefits without hindering development. Apply it during peak heat periods, such as midday in summer, or at the nursery stage for seedlings to prevent scorching.
Adjust coverage dynamically—increase to 50-60% during heatwaves and reduce to 30% in milder weather. Use a monthly rotation calendar and incorporate “shade rest days” for full sun exposure to prevent leggy growth. Gradually acclimate plants to more light as seasons change, removing temporary shade once they strengthen.
Why it matters: Proper timing prevents weak, spindly growth and helps harden plants for changing seasons.
How Shade Impacts Yield, Quality, and Water Use
Shade influences key aspects of plant health through scientific principles. It reduces water loss and thermal stress, improving yield and quality by minimizing sunburn on leaves and fruits. For example, it can lower evapotranspiration, cutting water needs by 30-40%.
However, potential downsides include increased humidity, which raises pest risks like aphids or mildew, and reduced yields in sun-dependent crops due to limited photosynthesis. Over-shading may also lead to spindly plants or disease susceptibility, so proper management is essential.
Contrarian view: Some gardeners argue that “more shade is always better,” but research shows that over-shading can actually stunt growth and reduce flavor in some crops!

Other Yield Improvement Practices
Shade works best when combined with complementary techniques. Start with soil preparation by amending with compost or manure to enhance water retention. Water shaded gardens less frequently to avoid root rot, and use balanced fertilizers for steady nutrients.
Pair shade with mulching to suppress weeds and conserve moisture, and ensure proper spacing for airflow to manage pests. Organic pest solutions and monitoring help mitigate humidity-related issues, creating a holistic approach that boosts yields.
Fun fact: Mulching + shade can cut your garden’s water needs in half!
Getting Started: Your First Steps Towards Shaded Success
- Source materials: Check local ag suppliers or online for shade cloth and frames.
- Learn from others: Join garden forums or X (formerly Twitter) for real-world tips.
- Experiment: Start small—try shading one bed and compare results.
- Adapt: Every garden is unique. Observe, tweak, and share your findings!
Embrace Shade for a More Productive Garden
Shade isn’t just a summer survival tactic—it’s a powerful tool for healthier plants, bigger yields, and sustainable gardening. By choosing the right crops, optimizing your shade setup, and integrating smart soil and water practices, you’ll be amazed at how much more your garden can produce. So why not try a little shade this season? Your veggies (and your water bill) will thank you!
P.S. Love garden hacks? Here’s a bonus tip: Try planting basil under your tomato trellis for natural shade and a flavor boost—plus, it keeps pests at bay!
Amazon and the Amazon logo are trademarks of Amazon.com, Inc, or its affiliates.


Hi there! My name is Prasenjit and I’m an avid gardener and someone who has grown a passion for growing plants. From my hands-on experience, I have learned what works and what doesn’t. Here I share everything I have learned.




